The Euphrates River Drying Up: Unveiling the Silent Crisis of Mysterious Desiccation and Urgent Call for Action
The Euphrates River Drying Up, an iconic waterway in the Middle East, is facing a crisis of immense proportions. In recent years, reports have surfaced indicating that the river is gradually drying up. This alarming development has significant implications for the region’s ecosystems, water availability, agriculture, and socio-economic stability. In this article, we delve into the causes and consequences of the Euphrates River drying up, examining the various factors contributing to this dire situation.
The Euphrates River: A Lifeline in Peri
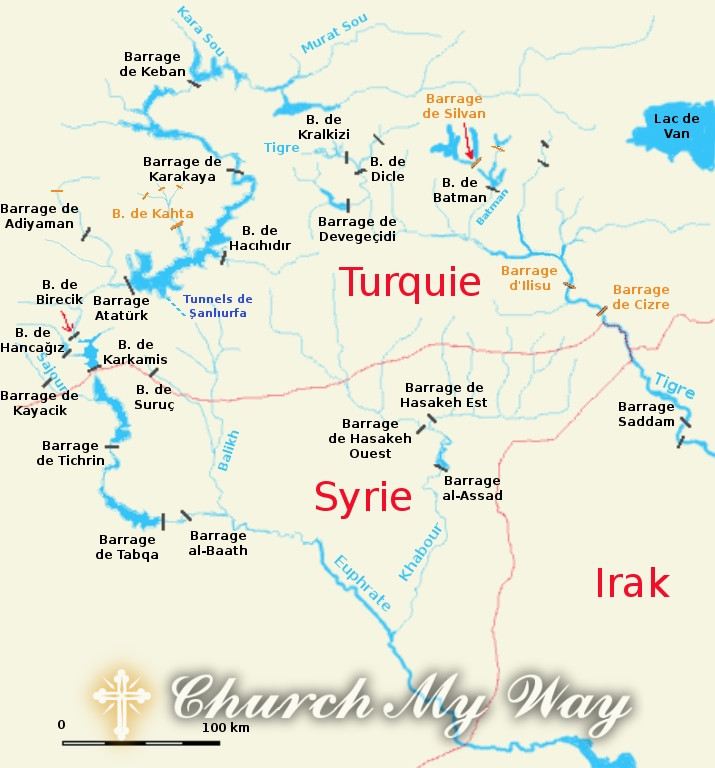
The Euphrates River has served as a vital lifeline for civilizations in the Middle East for thousands of years. It has been a source of sustenance, transportation, and cultural significance. The river spans multiple countries, including Turkey, Syria, and Iraq, and its waters have been used for agriculture, hydroelectric power, and domestic consumption. The Euphrates River holds immense importance for the civilizations that have thrived along its banks for thousands of years. It has served as a lifeline, providing sustenance, transportation, and a source of cultural significance. The river’s waters have been used for various purposes, including agriculture, hydroelectric power generation, and domestic consumption.
The importance of the Euphrates River
From ancient Mesopotamia to modern-day Iraq, the Euphrates River has shaped the development of societies and played a crucial role in their survival. Its fertile floodplains have supported agricultural activities, allowing civilizations to flourish and establish prosperous cities. The river has been a vital source of irrigation, enabling farmers to grow crops and sustain livelihoods. Moreover, the Euphrates River has facilitated trade and transportation throughout history. Its navigable waters have provided a means for the movement of goods, connecting different regions and fostering economic exchange. Communities along the river have relied on it for the transportation of goods, enabling commerce and cultural interactions.
Culturally, the Euphrates River holds significant symbolism and religious importance. It has been mentioned in ancient texts, including the Bible, as well as in Mesopotamian and Sumerian mythology. The river’s mythological and spiritual significance has influenced the beliefs and practices of civilizations that inhabited its surroundings. In summary, the Euphrates River is not merely a body of water; it is a vital artery that has sustained life, facilitated trade and shaped the cultural fabric of the Middle East for centuries. Its importance as a resource and a symbol cannot be overstated.
Declining water levels and the impact on ecosystems
Unfortunately, the Euphrates River is experiencing a rapid decline in its water levels. This has resulted in severe consequences for the region’s ecosystems. Wetlands and marshes that were once thriving habitats for diverse flora and fauna are now drying up. The loss of these ecosystems has led to the displacement and endangerment of several species, including migratory birds and endangered fish species.
Causes of the Euphrates River Drying Up
The drying up of the Euphrates River can be attributed to various causes, each playing a role in the gradual decline of its water levels. Understanding these causes is crucial in addressing the issue and implementing effective mitigation strategies. Here are five key factors contributing to the drying up of the Euphrates River:
- Climate change and changing precipitation patterns: One of the primary drivers of the river’s decline is climate change. Rising global temperatures have led to increased evaporation rates, resulting in the loss of water from the Euphrates River. Additionally, changing precipitation patterns have led to reduced rainfall and snowfall in the upstream regions, reducing the inflow of water into the river.
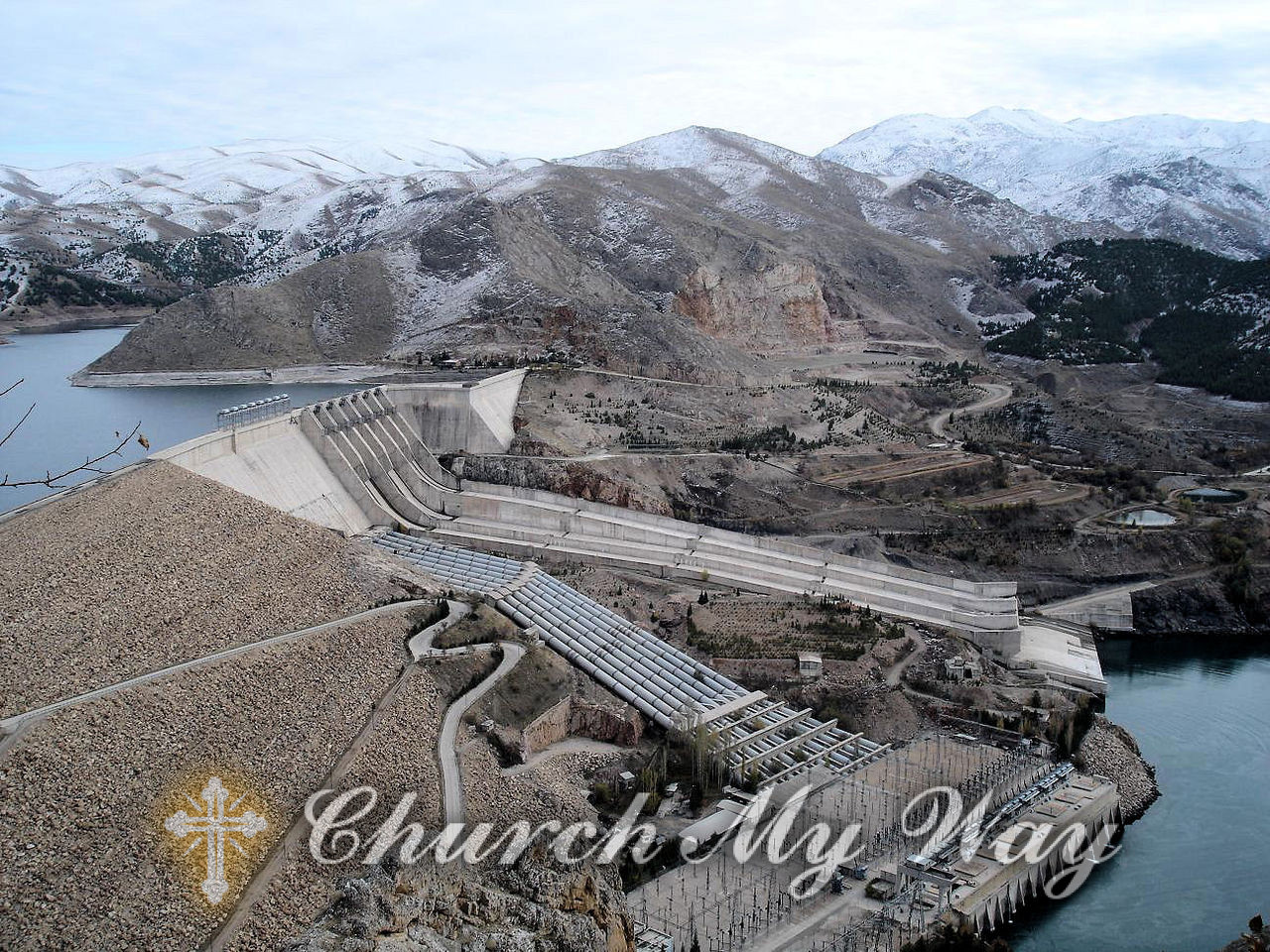
- Dams and water diversion projects: The construction of dams and water diversion projects along the course of the Euphrates River has significantly impacted its water flow. Countries such as Turkey have constructed large dams for hydropower generation and irrigation purposes. While these projects provide benefits such as electricity and water supply, they also reduce the downstream flow of water, affecting the river’s natural balance.
- Over-extraction of water resources: The excessive withdrawal of water from the Euphrates River for agricultural, industrial, and domestic purposes has further contributed to its drying. The increasing demands for water resources, coupled with inefficient water management practices, have put additional strain on the river’s already limited water supply.
- Deforestation and land degradation: The extensive deforestation and land degradation in the Euphrates River basin have had a negative impact on its water retention and overall ecosystem health. Deforestation reduces the river’s ability to retain moisture, leading to increased runoff and decreased water availability. Moreover, land degradation practices, such as unsustainable agricultural practices and soil erosion, further exacerbate the drying of the river.
- Political and geopolitical factors: Political tensions and conflicts in the region have hindered effective water management and cooperation among the countries sharing the Euphrates River. Disputes over water rights, competing interests, and a lack of comprehensive agreements have hindered the implementation of sustainable practices, aggravating the drying of the river.
Addressing these causes requires a multi-faceted approach that includes sustainable water management, climate change mitigation strategies, international cooperation, and efforts to promote responsible land use practices. By tackling these underlying factors, it is possible to mitigate the drying of the Euphrates River and ensure its long-term viability.
Climate change and changing precipitation patterns
One of the primary causes of the Euphrates River drying up is climate change. Rising temperatures in the region have led to increased evaporation rates, causing a reduction in the river’s water volume. Additionally, changing precipitation patterns have resulted in decreased rainfall and snowfall in the upstream regions, further exacerbating the issue.
Another significant factor contributing to the drying up of the Euphrates River is the construction of dams and water diversion projects along its course. Countries like Turkey have constructed large dams for hydropower generation and irrigation purposes, significantly reducing the downstream flow of water. This has disrupted the natural balance of the river’s ecosystem and further intensified its drying.
Consequences of the Euphrates River Drying Up
The drying up of the Euphrates River has far-reaching consequences that impact various aspects of the region’s environment, society, and economy. Here are five significant consequences of the drying up of the Euphrates River:
- Water scarcity and its impact on agriculture: The decline in water availability due to the drying up of the Euphrates River has led to water scarcity, particularly for agricultural purposes. Farmers who rely on the river for irrigation face significant challenges, resulting in decreased crop yields, reduced agricultural productivity, and increased vulnerability to drought. This, in turn, has severe implications for food security and the livelihoods of communities dependent on agriculture.
- Ecosystem disruption and loss of biodiversity: The drying up of the Euphrates River has disrupted ecosystems and caused the loss of biodiversity. Wetlands and marshes, once vibrant habitats for diverse flora and fauna, are drying up, leading to the displacement and endangerment of numerous species. Migratory birds, fish, and other wildlife that depend on the river for their survival are experiencing habitat loss and declining populations, further threatening regional biodiversity.
- Socio-economic instability and displacement: The drying up of the Euphrates River has socio-economic ramifications, particularly for communities along its banks. As water scarcity increases, livelihoods depend on agriculture and related sectors are at risk. Farmers face reduced incomes, increased poverty, and potential displacement, leading to social unrest and economic instability. Displaced communities may seek refuge in already densely populated urban areas, adding further strain on infrastructure and resources.
- Energy production challenges: The Euphrates River has been harnessed for hydroelectric power generation, contributing to the region’s energy supply. However, the drying up of the river reduces its ability to generate sufficient hydropower, impacting the reliability and availability of electricity. This can pose challenges for industries, businesses, and households that rely on a stable energy supply.
- Geopolitical tensions and conflicts: The dwindling water resources of the Euphrates River can exacerbate existing geopolitical tensions in the region. As countries compete for scarce water supplies, conflicts may arise, leading to strained relations and potential escalation. The geopolitical implications of water scarcity can have far-reaching consequences, destabilizing the region and hindering cooperation on other pressing issues.
To address these consequences, sustainable water management practices, efficient irrigation techniques, alternative water sources, and international cooperation are essential. By prioritizing the preservation and restoration of the Euphrates River’s water resources, it is possible to mitigate the socio-economic and environmental impacts associated with its drying up.
Water scarcity and its impact on agriculture
The drying up of the Euphrates River has severe implications for agriculture in the region. Farmers who rely on the river for irrigation face water scarcity, leading to crop failures and reduced agricultural productivity. This, in turn, affects food security, livelihoods, and the overall socio-economic stability of communities along the river.
Geopolitical tensions and conflicts
The dwindling water resources of the Euphrates River have the potential to exacerbate existing geopolitical tensions in the region. As countries compete for scarce water supplies, conflicts may arise, further destabilizing the already fragile political landscape. This could have far-reaching consequences for regional stability and cooperation.
Mitigation Efforts and Future Outlook
Efforts to mitigate the drying up of the Euphrates River and ensure its long-term sustainability are crucial for the well-being of the region. Here are several key mitigation strategies and a glimpse into the future outlook:
- International cooperation and sustainable water management: Addressing the complex challenges of the Euphrates River requires cooperation among the countries sharing its waters. Collaborative efforts should focus on implementing sustainable water management practices that balance the needs of all stakeholders. This includes equitable water allocation, efficient irrigation techniques, and the establishment of comprehensive agreements to manage water resources effectively.
- Promotion of alternative water sources: Exploring alternative water sources can help reduce the strain on the Euphrates River. This includes the adoption of desalination technologies to utilize seawater, as well as the implementation of rainwater harvesting and wastewater recycling systems. Diversifying water sources can enhance water security and reduce reliance on the dwindling river.
- Conservation measures and ecosystem restoration: Protecting and restoring the ecosystems surrounding the Euphrates River is essential for its ecological health and long-term viability. Conservation measures, such as reforestation efforts, land rehabilitation, and the preservation of wetlands, can help retain moisture, enhance water retention, and support biodiversity conservation. Restoring degraded habitats can also aid in the recovery of species affected by the river’s drying.
- Climate change adaptation and mitigation: Addressing the underlying issue of climate change is vital for the sustainable future of the Euphrates River. Mitigation efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions must be pursued alongside adaptation strategies to cope with the changing climate. This includes promoting renewable energy sources, implementing climate-resilient agriculture practices, and raising awareness about the importance of climate action.
- Community engagement and awareness: Engaging local communities and raising awareness about the importance of preserving the Euphrates River can foster a sense of responsibility and encourage sustainable practices. Education campaigns, community participation in water management decision-making processes, and the promotion of water conservation practices can empower individuals to contribute to the preservation of the river.
The future outlook for the Euphrates River largely depends on the collective efforts undertaken to address the drying phenomenon. By prioritizing sustainable water management, fostering international cooperation, and adopting innovative solutions, there is hope for the restoration and revitalization of the river. However, it requires sustained commitment, effective governance, and the recognition of the river’s ecological, cultural, and socio-economic significance.
While the challenges are significant, the Euphrates River has the potential to rebound and once again thrive, supporting the diverse ecosystems, livelihoods, and cultural heritage that depend on its waters. Through collaborative action and a shared commitment to its preservation, a sustainable future for the Euphrates River can be achieved.
International Cooperation and sustainable water management
Addressing the issue of the Euphrates River drying up requires international cooperation and sustainable water management strategies. Countries along the river must come together to find equitable solutions that ensure the long-term viability of the river’s resources while considering the needs of all stakeholders.
Alternative water sources and Conservation measures
To mitigate the impacts of the drying river, exploring alternative water sources and implementing conservation measures are crucial. Rainwater harvesting, wastewater recycling, and efficient irrigation techniques can help alleviate the strain on the Euphrates River’s dwindling water resources.
Conclusion
The drying up of the Euphrates River is a distressing development with far-reaching consequences. As climate change, dam construction, and water diversion projects continue to impact the river’s water levels, urgent action is needed to mitigate the environmental, social, and economic repercussions. By prioritizing sustainable water management and fostering international cooperation, we can work towards a future where the Euphrates River flows once again, sustaining ecosystems and livelihoods.
To mitigate these challenges, international cooperation and sustainable water management practices are paramount. Collaboration among countries sharing the Euphrates River is essential for equitable water allocation and the implementation of efficient irrigation techniques. Additionally, exploring alternative water sources, such as desalination, rainwater harvesting, and wastewater recycling, can help alleviate pressure on the river.
Conservation measures and ecosystem restoration efforts are crucial for preserving the river’s ecological health. By protecting wetlands, undertaking reforestation initiatives, and rehabilitating degraded lands, it is possible to enhance water retention and support biodiversity conservation.
Addressing climate change through both adaptation and mitigation strategies is vital for the future of the Euphrates River. Promoting renewable energy sources, climate-resilient agriculture, and raising awareness about the urgency of climate action are necessary steps.
Engaging local communities and fostering awareness play a pivotal role in sustainable water management. Education campaigns, community involvement in decision-making processes, and promoting water conservation practices empower individuals to contribute to the preservation of the river.
The future outlook for the Euphrates River hinges on the collective efforts undertaken to address its drying. Through sustainable practices, international cooperation, and innovative solutions, there is hope for its restoration and revitalization. By recognizing its ecological, cultural, and socio-economic significance, a sustainable future for the Euphrates River can be achieved.
FAQs
1. Can the drying up of the Euphrates River be reversed?
Reversing the drying up of the Euphrates River would require a concerted effort involving sustainable water management practices, climate change mitigation, and international cooperation. While challenging, it is not impossible with the right strategies in place.
2. How does the drying up of the Euphrates River impact wildlife?
The drying up of the Euphrates River has led to the loss of wetlands and habitats, endangering several species of wildlife, including migratory birds and fish. The disruption of ecosystems can result in the decline and even extinction of various plant and animal species.
3. What are the geopolitical implications of the drying Euphrates River?
The drying Euphrates River can lead to geopolitical tensions and conflicts among countries sharing its water resources. Competing interests and water scarcity may strain relations and destabilize the region, emphasizing the need for diplomatic solutions and cooperation.
4. How can individuals contribute to conserving the Euphrates River?
Individuals can contribute to conserving the Euphrates River by practicing water conservation in their daily lives, raising awareness about the issue, supporting organizations working towards sustainable water management, and advocating for responsible policies and practices.
5. What are some alternative water sources for the region?
In addition to the Euphrates River, alternative water sources for the region can include desalination plants, rainwater harvesting, wastewater recycling, and efficient irrigation systems. These measures can help reduce the strain on the river and ensure water availability for various purposes.
References & Pictures:
- The World Bank. (2021). Managing Water Resources for Sustainable Development in the Euphrates and Tigris River Basins. Retrieved from https://www.worldbank.org/en/news/feature/2021/04/12/managing-water-resources-for-sustainable-development-in-the-euphrates-and-tigris-river-basins
- United Nations Development Programme. (2018). Drying Euphrates River Threatens Iraq’s Future. Retrieved from https://www.undp.org/content/undp/en/home/news-centre/news/2018/drying-euphrates-river-threatens-iraqs-future.html
- Arslan, A., et al. (2020). Implications of Climate Change on the Euphrates–Tigris Basin Water Resources. Water, 12(10), 2944. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102944
- Majeed, S. (2019). Analysis of Hydrological and Environmental Changes of the Euphrates River in Iraq. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(17), 17541-17559. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05375-9